The Sequencer’s Role
The sequencer serves as:
- A controller for generating and managing sequences of transactions.
- An arbiter for sequences running simultaneously, decides which sequence of the running sequences should pass its transactions to the driver.
- the sequencer_Id is a field assigned by the sequencer to each sequence
- within each sequence each transaction is assigned a unique Id
- so each transaction is uniquelyidentified by the combination of its seq_id and tr_id
- it is the sequencer responsibility to route the drivers responses correctly to the correct sequence based on the sequence_Id and tr_Id
For this, the sequencer must:
- Send transactions to the driver.
- provides implementation of the API
- Optionally receive feedback from the driver (e.g., when the driver requests the next transaction or sends status updates).
3. Why Use an Export?
The sequencer connects to the driver via a TLM interface (typically uvm_seq_item_pull_imp in TLM1). The sequencer needs an export because the driver calls methods implemented in the sequencer. Here’s how it works:
- Driver Pulls Transactions:
- The driver initiates communication by pulling transactions from the sequencer via the
default_export. - يعني الدرايفر هو اللي بيبدا التواصل عشان كده ال API Implementation هيكون عند ال sequencer
- Using an export ensures the sequencer provides the required TLM implementation (
get_next_item(),item_done(), etc.).
- The driver initiates communication by pulling transactions from the sequencer via the
- Driver Requests and Sequencer Responds:
- With an export, the driver can act as the active entity that makes requests (
seq_item_port.get_next_item()), and the sequencer fulfills these requests.
- With an export, the driver can act as the active entity that makes requests (
- Bidirectional Communication:
- The sequencer provides callbacks (like
item_done()) so that the driver can notify it when a transaction is complete or needs arbitration. - An export allows the driver to trigger these callbacks.
- The sequencer provides callbacks (like
5. Summary of Responsibilities
| Component | Interface Usage | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Driver | Port | Actively requests transactions from the sequencer. |
| Sequencer | Export | Reactively provides transactions to the driver and implements TLM methods. |
The Sequence Role
- just to generate transactions
- each transaction has a unique tr_id and each sequence has a unique seq_id
- all that done inside the body() task of the sequence class
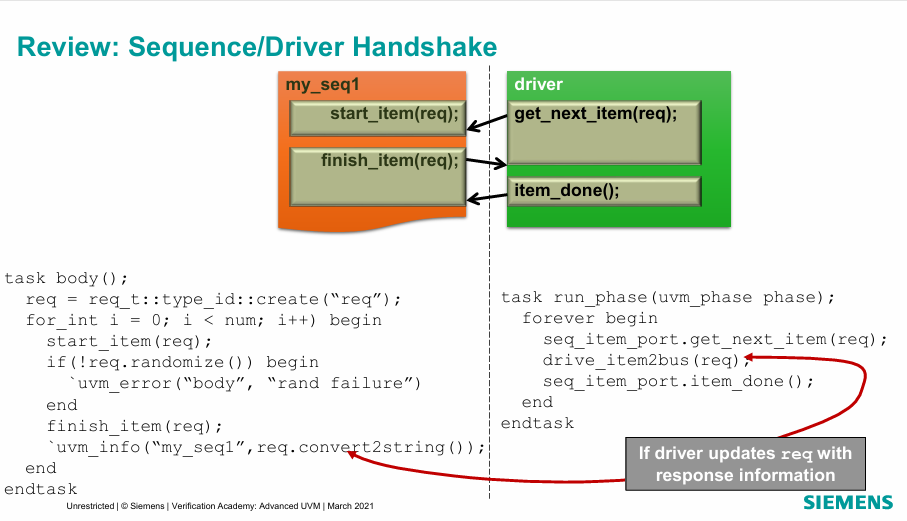
Mechanism
- the sequence class generate the transaction inside the body() task and call start_item()
- the start_item() blocks the execution in the body() untill the get_next_item() executed from the run_phase in the driver this indicates that the driver is ready to receive a transaction
- the start_item() unblocks and finish_item() executed which sends the transaction to the driver
- the item_done() in the run_phase at the driver indicates that the driver completed his job
Key Points:
- The sequence is the active component responsible for generating transactions.
- The sequencer is a reactive component that:
- Arbitrates between sequences (if there are multiple).
- Passes the next transaction to the driver upon request.
- The driver is also reactive and:
- Requests transactions from the sequencer.
- Drives the transactions to the DUT.
Example Flow
Imagine a testbench with one sequence, one sequencer, and one driver:
- The sequence generates a transaction (e.g., a write operation with specific address/data).
- The sequencer holds the transaction in its queue.
- The driver calls
seq_item_port.get_next_item()to fetch the transaction. - The driver processes the transaction (e.g., sends it to the DUT via an interface).
- Once done, the driver calls
item_done()to notify the sequencer. - The sequencer acknowledges and allows the sequence to generate the next transaction.
Arbitration (When Multiple Sequences Run)
If multiple sequences are active, the sequencer uses arbitration logic (e.g., round-robin, priority-based) to determine which sequence gets to send its transaction to the driver.
3. add_typewide_sequence(sequence_x.get_type());
- Purpose:
- Registers a typewide sequence for this class or component.
- A typewide sequence is a special mechanism in UVM that allows you to associate a default sequence with a sequencer. This sequence will be automatically started when the test begins, unless explicitly overridden.